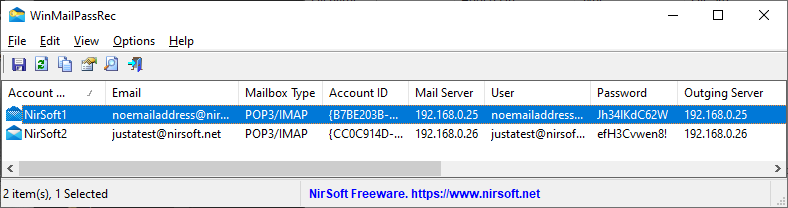
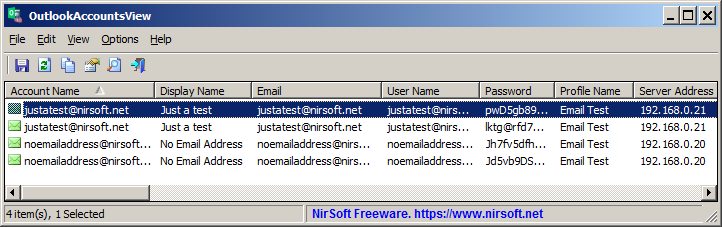
Some of the password-recovery tool on NirSoft Web site allows you to decrypt passwords stored on external hard drive plugged to your computer.
If the passwords are encrypted with the DPAPI (Data Protection API) system, you may need to type your login password, because the login password is used
to decrypt the encryption key, and without the login password it’s impossible to recover the passwords instantly.
However, if you login with your Microsoft account (On Windows 10 and Windows 11), the login password is not used anymore.
Instead of the login password, Microsoft generates a random 44-characters password for your Microsoft account, and this password is used in the DPAPI encryption process instead of the login password.
So if you want to recover from external drive the DPAPI passwords created under Microsoft account , you have to provide the random password generated for your Microsoft account instead of the login password.
You can get this random password by using the new MadPassExt tool.
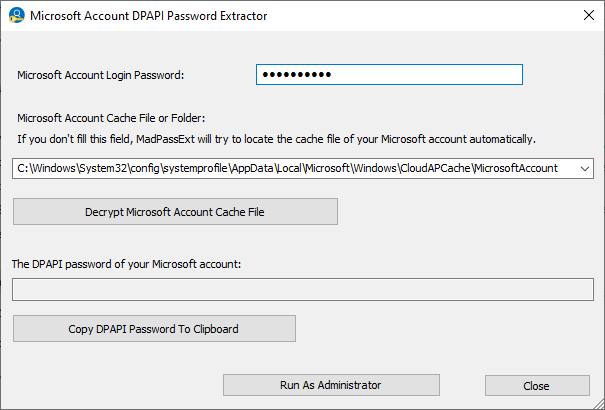
The new MadPassExt tool
The MadPassExt tool decrypts the cache file of your Microsoft account, located under C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\CloudAPCache\MicrosoftAccount ,
and extracts the randomly generated password needed to decrypt DPAPI-encrypted passwords stored on external drive.
This cache file is created when you login into Windows 10 and Windows 11 with your Microsoft account.
In order to decrypt the Microsoft account cache file, you have to provide the actual login password of your Microsoft account.
The new MadPassExt tool is available to download from this Web page.