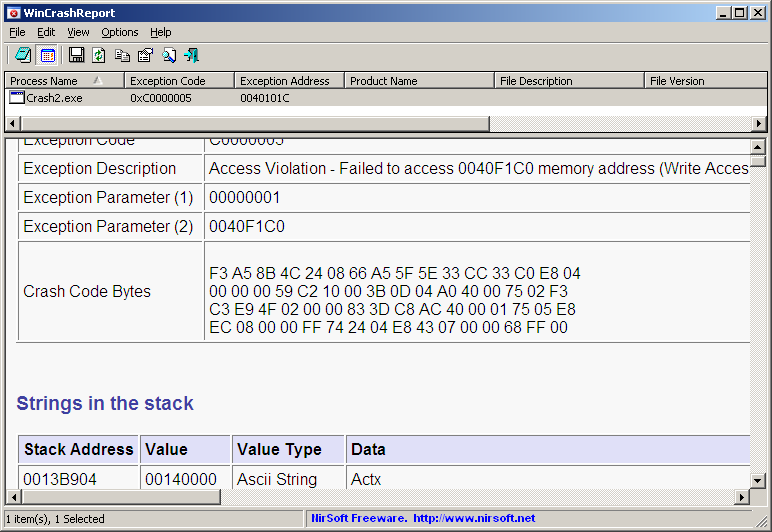
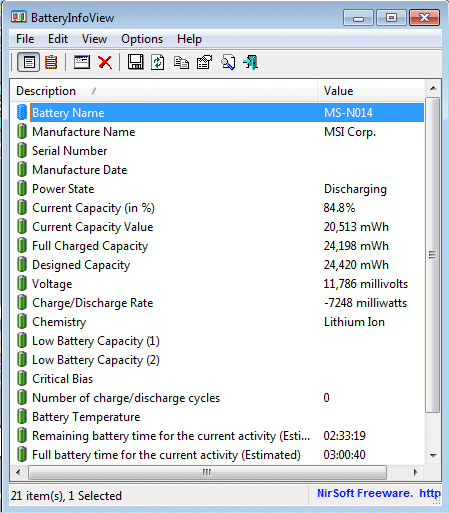
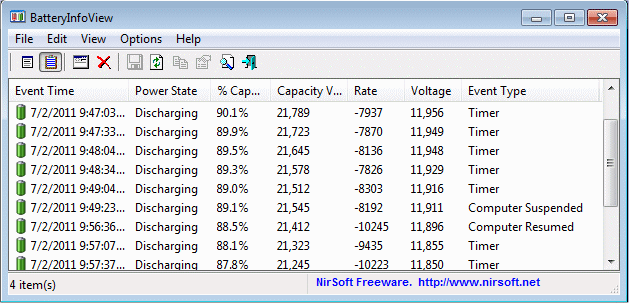
WinCrashReport is a new utility that provides an alternative to the built-in crash reporting program of Windows operating system. When application crashes in your system and Windows displays the internal crash window of the operating system, you can run WinCrashReport, and get extensive report about the crashed application. The crash report of WinCrashReport is displayed as simple text or in HTML, and includes the following information: Crash memory address, Exception code, Exception description, Strings found in the stack, call stack, processor registers, modules list, threads list, and more…
As opposed to Microsoft crash reporting module, which behaves differently from one version of Windows to another, WinCrashReport allows you to get the same report format for all versions of Windows, starting from Windows 2000 and up to Windows 7. It also allows you to easily save the crash report into text file or HTML file.
For more information this new utility, click here.